

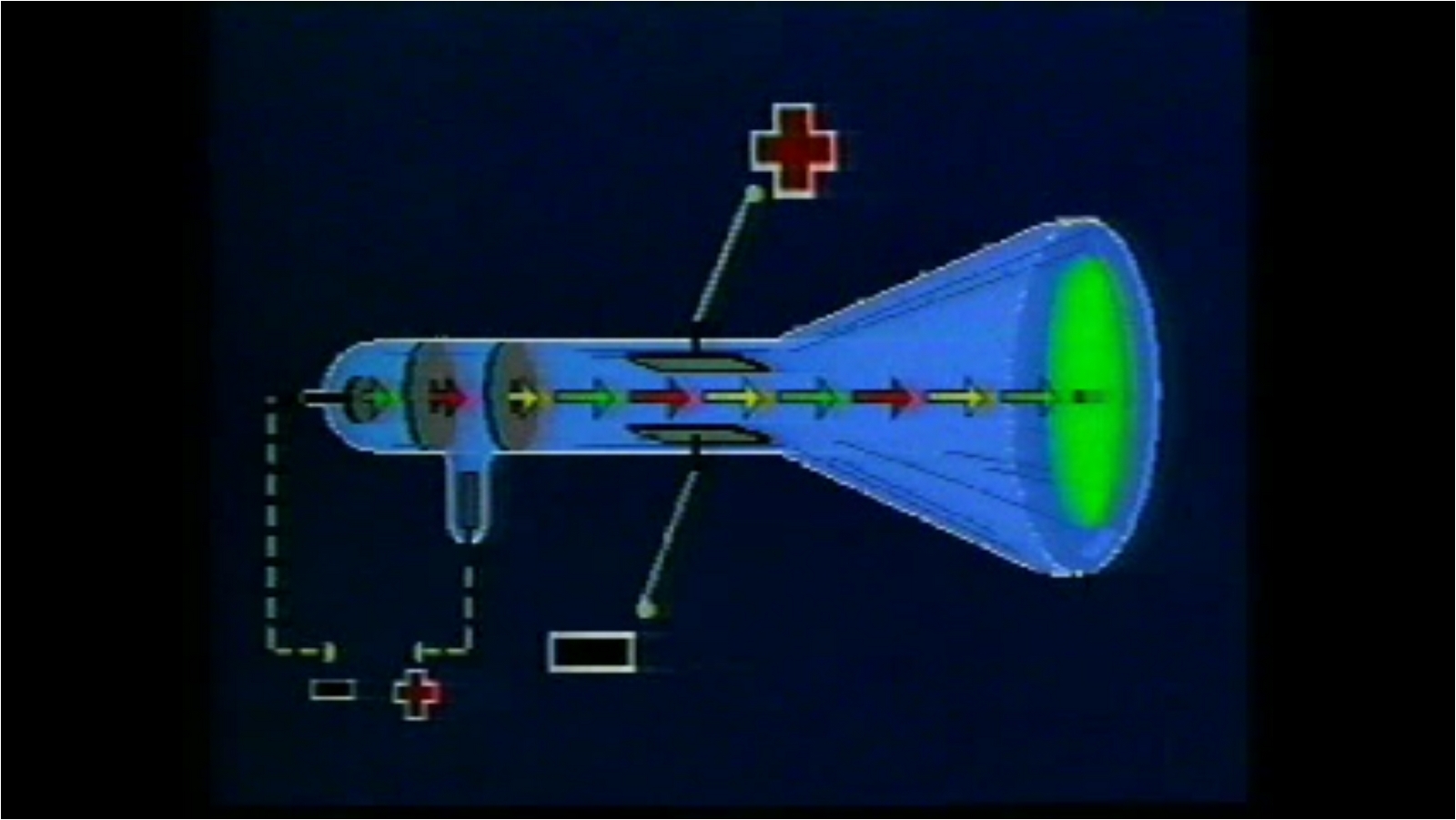
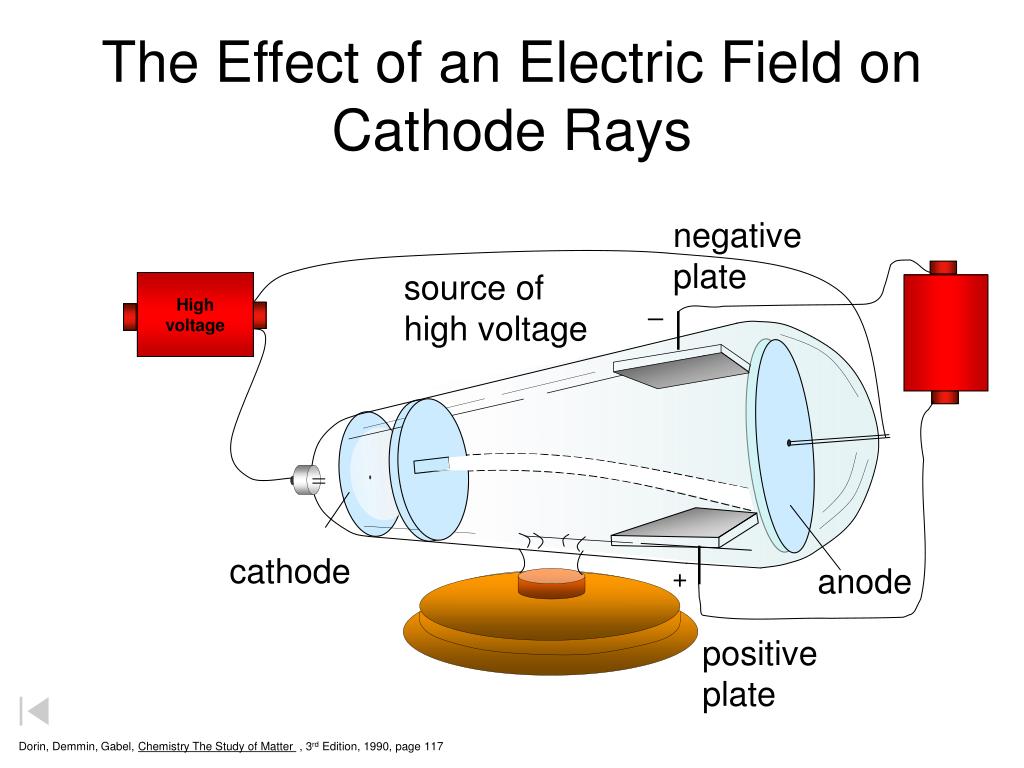
In the first, the magnetic effect on cathode rays was studied while in the second, the rays were deflected by an electric field. His entire works can be divided into three different experiments. He concluded that the rays were comprised of particles. The immaterial nature and the aetherial hypothesis of cathode rays were proved wrong by J. According to some, the rays are due to some process in the aether. Many diverse opinions were held on these rays. Phosphorescent coating: It is the final part of the CRT, where the rays strike to create a glow.īack in those days, physicists were unclear whether cathode rays were immaterial like light or were material.Cathode rays bend as they interact with these fields. This is achieved by an external electric and magnetic field. Deflection system: It controls the direction of the electron beam.It will narrow the beam and increase its kinetic energy.
Cathode ray experiment when series#
Focusing and accelerating system: It is made up of a series of anodes.However, cold-cathode emission mechanism was used in Thomson's experiments. In modern CRTs, the electron beam is generated by thermionic emission-using a heating filament-as shown in the above diagram. It emits the sharp electron beam, cathode rays. Electron emitter (or electron gun): The electron gun comprises of primarily heater and cathode.The air in the tube is pumped out to create a vacuum. The cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a hollow glass tube. These rays travel in straight lines and can be deflected by electric and magnetic field. What are cathode rays? Cathode rays are streams of electrons emitted from the cathode (the electrode connected to the negative terminal of a battery). His experimental results were further investigated by Rutherford and Bohr, which further provided important insights into the atomic world.īefore directly jumping Thomson's findings, let us understand some basic knowledge on cathode rays and the cathode-ray tube. However, Thomson's contributions remain more significant than the rest. Thomson was not the only one working on cathode rays, but several other players like Julius Plücker, Johann Wilhelm Hittorf, William Crookes, Philipp Lenard had contributed or were busy studying it. The apparatus of his experiment is called the cathode-ray tube (CRT). These particles later were named electrons. In 1897, he showed that cathode rays were composed of very small negatively charged particles. He was well-known for the discovery of the electron. Sir Joseph John Thomson was a British physicist and Nobel Laureate.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
